The bad news: Alberta pipeline spills 60,000 liters of crude oil into muskeg.
The spin: As usual, the industry and its government partners assure us that “clean-up efforts are underway.” What else can they say, spill after spill…
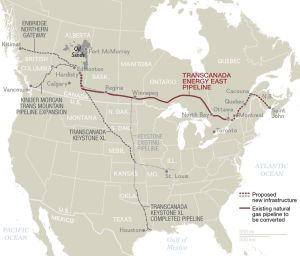
Tar sands pipelines. Image: newrepublic.com
The worse news: The industry is poised to send millions of gallons of this muck via pipelines and trains across thousands of kilometres/miles through every kind of terrain and aquifer to the west and east coasts, and south through the US.
The good news: Every step of the way, courageous people are resisting.
At Burnaby Mountain in British Columbia, more than 100 resisters have been arrested to date for trying to block a scheme by the Texas-based Kinder Morgan corporation to ram a pipeline through the mountain.
Canada’s National Energy Board granted the company rubber-stamp approval to proceed with test drilling, despite the fact that the pipeline will cross – invade, actually – territory which the Indigenous First Nations have never legally ceded to either the federal or provincial government.
In May, the Tsleil-Waututh Nation launched the first Indigenous legal challenge to oil sands pipelines crossing B.C., in a direct challenge to the National Energy Board’s deeply flawed ‘review’ process.
Last week, a provincial court judge threw out the charges against the Burnaby Mountain resisters, which included both First Nations and non-First Nations citizens.
Unfortunately, the judge’s ruling was based on Kinder Morgan having provided inaccurate GPS boundaries for its drilling sites, which leaves the company free to get a new revised injunction against the resisters.
Stakes for resisters also rose sharply when Kinder Morgan launched a $5.6 million lawsuit against several resisters and two university professors who have spoken out against the company’s pipeline test work on Burnaby Mountain.
Still, as the enormity of the threat become more and more apparent, resistance continues to grow across the continent. It takes many forms. This past week, Concordia University in Montreal became the first Canadian university to start divesting from fossil fuels.
For a scientist’s insight on the tar sands and climate change, see chapter 9, in Bold Scientists. Read an excerpt here. Scroll down to ‘Pesky data.’




 Photo: Aurora Cooperative
Photo: Aurora Cooperative